ArdorComm News Network
June 29, 2023
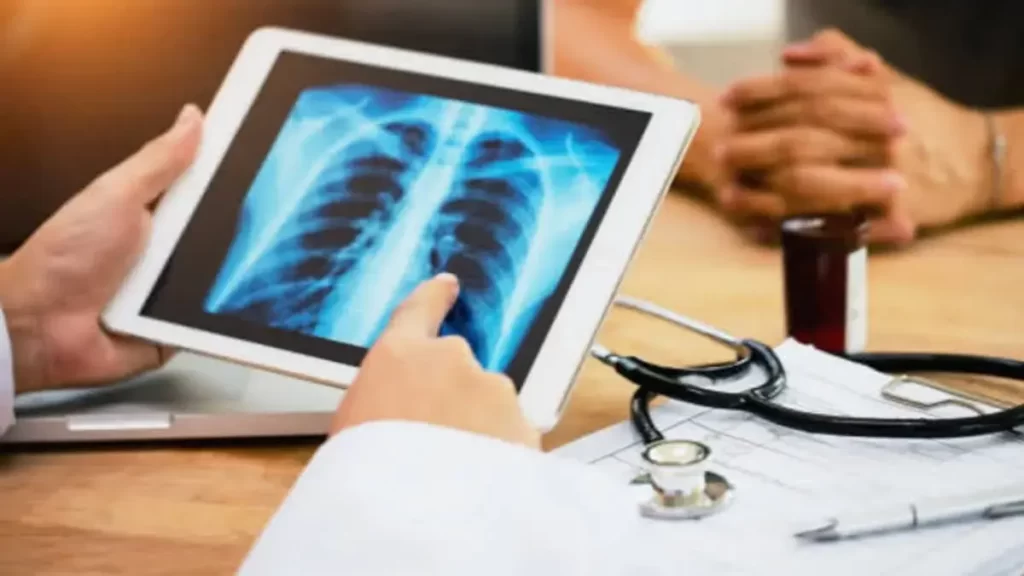
A recent study published in the Radiology journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) has revealed that the assistance of a highly accurate artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm significantly improves the detection of lung cancers in chest X-rays. Moreover, the study found that the integration of AI suggestions also enhances human acceptance of AI in the diagnostic process. While AI-based image diagnosis has made significant progress in medicine, there has been limited exploration of the factors influencing radiologists’ diagnostic decisions when utilizing AI-assisted image reading.
Researchers from Seoul National University conducted a retrospective study involving 30 readers, including 20 experienced thoracic radiologists and 10 radiology residents. The readers assessed 120 chest X-rays without the aid of AI. Among the X-rays, 60 were from lung cancer patients, and 60 were controls. In a subsequent session, each group re-evaluated the X-rays with the assistance of either a high-accuracy or low-accuracy AI, without knowledge of the use of different AIs. The study found that the use of high-accuracy AI significantly improved the readers’ detection performance compared to low-accuracy AI. Additionally, the implementation of high-accuracy AI resulted in more frequent changes in the readers’ determinations, indicating their susceptibility to AI recommendations.
Dr. Chang Min Park, the lead author of the study, suggested that the substantial sample size might have contributed to the readers’ confidence in the AI’s suggestions. The researchers observed that human trust in AI played a crucial role in their susceptibility to AI recommendations. Compared to the initial reading session, readers supported by the high-accuracy AI during the second session exhibited higher sensitivity and specificity in detecting lesions. However, there was no improvement in these measurements when readers were assisted by the low-accuracy AI.
Dr. Park emphasized that AI can assist radiologists effectively only when the AI’s diagnostic performance equals or surpasses that of human readers. The study highlights the importance of utilizing high-performance AI in clinical practice. Nevertheless, Dr. Park acknowledged that the definition of “high diagnostic performance AI” may vary depending on the task and clinical context. The study underscores the need for the development of high-performance AI models tailored to specific tasks and the corresponding clinical settings.
The researchers plan to expand their investigation of human-AI collaboration to detect other abnormalities in chest X-rays and CT images in the future.