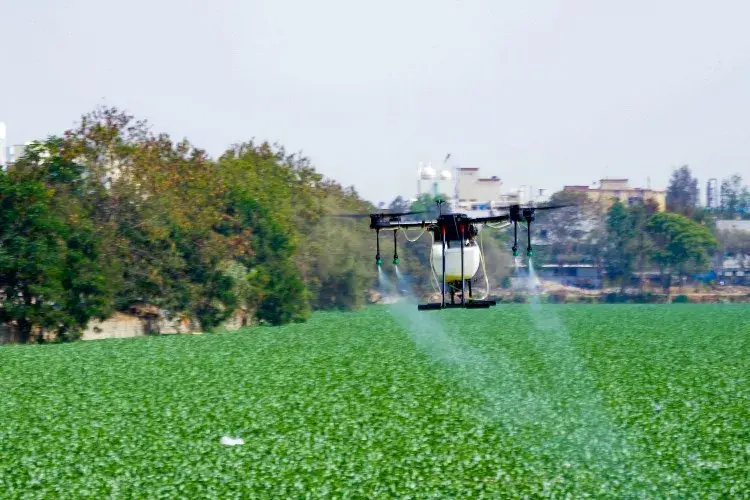
The initiative by the Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) to utilize drones for mosquito fogging in areas prone to breeding these insects has faced delays despite a trial run conducted last week. According to a recent report from the MCD released on Monday, there were 105 new cases reported last week up until Saturday, whereas the entire month of July had seen 121 cases. The drone project was temporarily suspended due to safety concerns leading up to Independence Day, as stated by an official. The official further explained that all preparations have been made for the drone initiative, and the plan is to kick off the operation after August 15th. Each drone is capable of carrying 30 liters of insecticide, which would enable the targeted spraying of hard-to-reach areas like lakes, canals, and riverfront vicinity. The focus of this effort is to combat mosquito breeding in such areas. A notable trial run took place on August 1st, where the public health department employed a drone to spray anti-larvae mixture in the Usmanpur region. This trial aimed to address areas with a high concentration of dengue cases reported during the previous week. The cumulative count of dengue cases in the city has reached 348 so far, as opposed to 174 cases in 2022, 22 cases in 2021, 35 cases in 2020, and 47 cases in 2019. The situation underscores the concern, especially given the previous year’s total of 75 cases in the entirety of August, 72 cases in 2021, and 47 cases in 2020. Authorities noted that mosquito breeding has been exacerbated in outer Delhi regions due to waterlogging. The official emphasized that community support is crucial to effectively address this issue and urged everyone to prevent waterlogging in their surroundings and terraces. Moreover, instances of malaria have seen a significant rise, with a total count of 85 cases compared to 35 cases in 2022, 24 cases in 2021, and 45 cases in 2020. Thirteen malaria cases were recorded in the past week alone, as per the official. However, the occurrence of chikungunya has been relatively low, with only one case reported last week and a total of 15 cases, contrasting with nine cases in 2022 and 13 cases in 2021. To combat the spread of vector-borne diseases, the MCD has launched a comprehensive campaign. This initiative involves training and deploying a specialized workforce, including Asha workers, safai karamcharis (sanitation workers), and nullah beldars (drainage workers). These efforts will complement the work of 3,000 domestic breeding checkers. Each ward will now have a dedicated team of three nullah beldars and three safai karamcharis who are trained to identify and eliminate potential breeding grounds for disease-carrying vectors, the official stated.